1.Explain the economic problem of an economy.
The economic problems of an economy are :
a)Human wants are unlimited
b)There are limited resources to satisfy these wants.
c)Unlimited wants have to be fulfilled with limited resources.
Therefore the economy faces the problem of satisfying unlimited wants with limited resources by arranging its wants in the order of priority in which it has to be fulfilled.From these arises the question of what to produce, how to produce and for whom to produce.
a)What to produce: Since resources are limited an economy has to produce those commodities which are high on its list of priorities. Only if this is done will there be a greater satisfaction of wants. If resources were unlimited the question of what to produce would not arise at all. If the economy makes a mistake of producing the wrong commodities then there will be wastage as the commodities produced will not be able to satisfy wants and will have to be thrown away. What to produce also depends on the pattern of consumption. For example in North India people consume more wheat while in South India people consume more rice.
b)How to produce: Not only the economy has decide on what to produce but has to decide on how much of each commodity it has to produce. If the wrong quantities are produced then there will be wastage of scarce resources. Once it has been decided how much to produce then the question of how to produce also has to be answered. If the level of technical knowledge is high then an automated method of production can be used else manual production methods have to be used. The quantity of production will depend on the method of production. How to produce will also depend on the resources available. For example if labour is easily available then a manual method may be used else a mechanized method has to be used.
c)For whom to produce: Every part of the economy has different wants and different level of resources. So the economic question is what has to be produced for whom. This is a problem of distribution. For example if the amount of wheat that can be produced is limited, then should it be distributed through Fair Price Shops ( Ration Shops) or sold for the more affluent people through regular shops.
2.Explain the factors that lead to economic problems.
The factors that lead to economic problems are:
a)Human wants are unlimited
b)The resources available to satisfy these are limited.Not only are human wants unlimited but wants keep increasing over a period of time.Further, as soon as on want is satisfied other wants crop-up. The main factor that lead to economic problems, therefore, is how to satisfy unlimited wants with limited means.
3.What do you understand by and economic problem? Can you think of an economy without and economic problem? Explain your answer.
An economic problem is a problem of too many wants and too few resources available to satisfy these wants. An economic problem can also be explained as the problem of what to produce, where to produce, how to produce and how much to produce. There is no economy without economic problems.
However, different economies have different economic problems. For example some part of Africa’s main economic problem is the scarcity of food and the non-availability of resources to produce the required food. The United States of America faces the problem of very high consumption of consumer goods. It faces the economic problems of people borrowing to consume. This leads to default in the repayment of loans. Default in repayment of loans leads to the economic problem of bankruptcy of financial institutions. A country like Singapore faces the economic problem of a shortage of skilled manpower. Every country faces its own economic problem.
There cannot be any economy without any economic problems. This is because no country has unlimited supply of resources. In order to meet their needs, each country has to depend on the resources of other countries. Even the USA has to depend on oil imported from the Middle East. Economic problems cannot be solved but restricted through good economic policies.
4.“Scarcity is the root of the problem of choice which every economy has to face? Discuss.
Scarcity is the root problem of choice which every economy has to face. This is because every economy has unlimited wants but only limited resources to satisfy these wants. All wants cannot be satisfied only because of limited resources.
Therefore, in order to satisfy wants, wants have to prioritized into important and less important want. Limited resources are then used to satisfy the more important wants first. If resources were not limited then all wants could have been satisfied together.Therefore, scarcity is the root problem of choice which every economy has to face.
5.Explain the central problems of an economy. Do all economies have similar central problems.
The central problems of an economy are as under :
-What and how much to produce: Every economy has to decide what to produce and how much to produce. What to produce has to be decided because limited resources cannot produce everything that is required. Only those goods which can satisfy the wants of the people better must be produced. Every economy has to decided how much of its resources must be used to produce guns and how much of it must be use to produce food. Not only that, each economy has to decide how much of each good is to be produced. If it is produced too little then there will be unfulfilled wants. If too much is produced then there will be wastage.
- How to produce : The economy must also decide how to produce. It has to decide on the choice of the technique of production. Each economy has to use a combination of resources like land, labour and capital to produce in a most efficient manner. The combination of resources used also depends upon the level of technical knowledge available in the county. If the level of technical knowledge is high then more capital and less labour may be used for production. If manpower is cheap then more manpower may be used.
-For whom to produce: This is a problem of distribution. The sum total of goods produced in the country is distributed among its population. Goods are produced for those who can afford to buy them.
-Fuller utilization of resources: Since resources are scarce, the available resources have to be fully utilized. Not utilizing resources is a waste of scarce resources. For example unemployment is a waste of scarce labour resources. Unemployment of scarce resources means the capacity to produce scarce goods goes waste and the economy does not get the benefit of the goods and services that could have been produced with these resources.
-Efficiency in utilization of resources: Each economy has to use resources efficiently. Efficient use of resources will avoid the wastage of scarce resources. Efficiency in the use of resources is defined as “when the economy cannot produce more of one commodity without producing less of another.”
-Economic Growth : Every economy faces the problem of economic growth. Every economy has to increase its ability to produce more goods and services with the available resources. If there is higher economic growth then the standard of living of people will improve. Economic growth is measured in term of Per Capita Income.
These central problems of an economy are common to all economies. Only the
method of resolving these varies from economy to economy. In a capitalist
economy these are resolved with the help of the “price mechanism”. In a socialist
economy these are resolved by the Central Planning Authority.
6.What is a production possibility curve? Upon what assumptions is it based? Explain its characteristics (shape).
A Production Possibility Curve is a diagram, which slopes downwards towards the right which explains nature of economic problem which arises due to the scarce resources which has alternate uses. It states schematically how much of two different commodities the society can produce with available resources. The assumptions of the Production Possibility Curve are:
- The amount of resources a society has is fixed.
- There is no change in technology.
- All productive resources are fully employed.
- Resources are not equally efficient in the production of all goods.
The characteristics (shape ) is :
-It slopes downwards towards the right : This indicates that that economy may give up the production of some items in order to produce some others. This is assuming that only limited resources are available and are utilized in the best manner.
- It is concave from the origin: The concave nature of the curve indicates the increasing opportunity cost. The opportunity cost of one commodity is the units of the other commodity which cannot be produced in order to produce one unit of a commodity. The opportunity cost keeps increasing since available resources cannot produces all goods with the same efficiency.
7.Illustrate the central problems of an economy with the help of production possibility curve.


The central problem of an economy are:
-what to produce.
-how much to produce
-for whom to produce
-economic growth.
The central problem can be explained with the help of the Production Possibility curve given above. According to the curve above, the economy, with the help of the available resources can either produce 12 units of food or 12 units of computers. According to the production possibility curve the same resources can be used to produce 11 units of food and a 5 units of computers. The other option is to produce 10 units of food and 6 units of computers. The opportunity cost of producing one additional unit of a computer is 1 unit of food. However, the opportunity cost of producing 10 instead of 9 computers (1 additional computer) is 3 units of food.
Thus, the Production Possibility curve indicates at what level the production is the most efficient leading to a better utilization of scarce resources.
8.Draw and define a production possibility curve and show the following situations on the diagram.
i.Full employment of resources.
ii.Under utilization of resources
iii.Growth of resources.
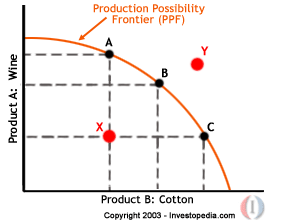
The Production Possibility Curve (PPC) represents the point at which an economy is most efficiently producing its goods and services and, therefore, allocating its resources in the best way possible. If the economy is not producing the quantities indicated by the PPC, then resources are being managed inefficiently and the production of society will dwindle. The Production Possibility Curve shows there are limits to production, so an economy, to achieve efficiency, must decide what combination of goods and services can be produced.
Let's turn to the chart above. Imagine an economy that can produce only wine and cotton. According to the PPF, points A, B and C - all appearing on the curve - represent the most efficient use of resources by the economy. Point X represents an inefficient use of resources, while point Y represents the goals that the economy cannot attain with its present levels of resources.
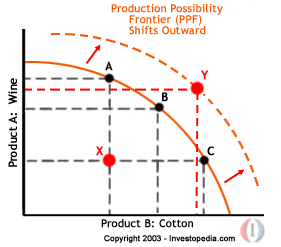
The outline of the curve (marked Production Possibility Frontier) represents full utilization of resources. Point Y in the chart (below) represents growth in the economy. More goods and services are being produced with a better utilization of resources.
However, point X in the chart above represents a point where resources are not being utilized properly.
9.What is meant by economic growth? Differentiate between economic grow and
economic development.
Economic growth is defined as the increase in the per capital income of the country. The total production of good and services in an economy is termed as Gross National Product (GNP). However, increase in the GNP does not represent economic growth. This is because if there is GDP increase along with an increase in population then there is no real growth. Therefore, economic growth is defined as the increase in the per capita income. An increase in the per capital income leads to greater availability of goods and services in the hands of the people. Further, economic growth is in expressed in real terms. That is, per capita income has to be adjusted for inflation and must be for a sustained or prolonged period of time.
Economic development is different from economic growth. There may be economic growth by way of high increase in the per capita income. However, this per capita income may be concentrated in the hands of a few people. If this happens then there is no improvement in the standard of living of the people. Further the increase in the per capital income may be offset by inflation. Therefore, economic development is a long term growth of per capital income accompanied by reduction of poverty, inequality and unemployment. It includes improvement in material welfare, eradication of poverty, removal of illiteracy, disease and low lifespan.
10.Explain the concept of economic development.
Economic development is different from economic growth. There may be economic growth by way of high increase in the per capita income. However, this per capita income may be concentrated in the hands of a few people. If this happens then there is no improvement in the standard of living of the people. Further the increase in the per capital income may be offset by inflation. Therefore, economic development is a long term growth of per capital income accompanied by reduction of poverty, inequality and unemployment. It includes improvement in material welfare, eradication of poverty, removal of illiteracy, disease and low lifespan.
-Economic development is growth plus improvement in the standard of living.
-Economic growth refers to output. However, economic development refers to the composition of output an allocation of resources to the different sectors of the economy.
-Economic growth refers to the rise in income. However, economic development also refers to reduction in poverty, inequality, income and unemployment.
-Economic growth refers only to the indicator of income. Economic development also refers to non-economic indicators like literacy, health services etc.
-Economic growth is relatively easy to realize. However, economic development involves a lot of changes in society. It involves changes in social structure, attitudes, institutions as well as acceleration of economic growth, eradication of poverty etc.
-Economic growth does not require as much government intervention as economic development. Economic development involves uplifting the living standards of the people of the country and therefore requires government intervention.
11.Explain briefly the different stages of economic growth.
The different stages of economic growth are:
a)Traditional Society: A traditional society is a stage of economic growth where there is absence of modern science and technology. There is low output and productivity and primitive methods of production. There is very low savings and investments. Agriculture is the most important activity of the society.
b)Pre-take off stage: In this stage some conditions for growth are created. People aspire for a higher standard of living. Values, social attitude and expectations of the people change. Enterprising people come forward to take risks. Investment in transportation and communications increases. There is an expansion of internal and external trade.
c)Take-off stage : Here the process of economic growth becomes self sustained. Growth takes place without much government interaction. There is a political revolution and a significant increase in savings and investment.
d)Drive to maturity : The economy becomes mature with a high level of per capita output. There is sustained economic growth over decades. Modern technology is applied to all sectors. Investment is over 10% of national income.
e)Age of mass consumption : This is the final stage of economic growth. The per capita income is high with a high standard of living. There is extensive use of consumer goods and use of house-hold gadgets. The attention of society moves from problems of production to problems of consumption.
1 comment:
The ISC Economics Handbook Class 12 by Nageen Prakashan is a helpful guide for students. It covers all the important topics in a simple way, making it easier to understand and score well in exams. Buy now today!
Post a Comment